Today, we will explain the common low-voltage electrical components in data center infrastructure, covering product performance analysis, interpretation of common standards, common questions in practice, application scenarios and selection, etc. Let’s start the journey of unveiling low-voltage electrical appliances together!
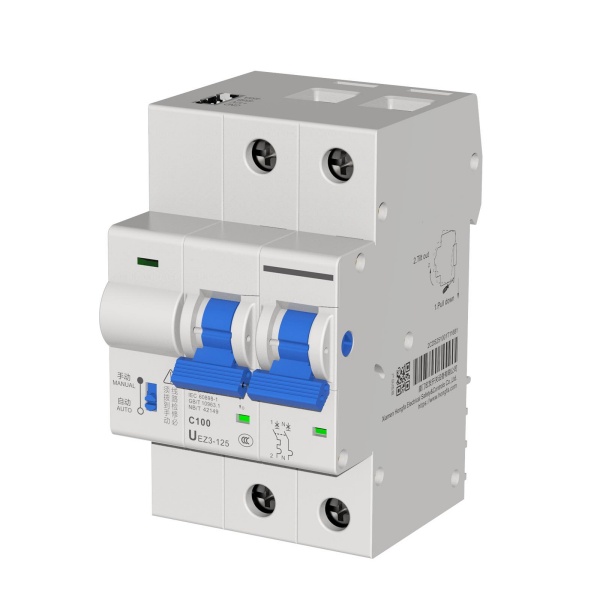

UEZ3-125 Intelligent Miniature Circuit Breaker
Miniature circuit breakers, also known as Miniature Circuit Breakers (MCB) in English, are the most common component products in the low-voltage electrical appliance product family. The end-users are generally exposed to the scene for the protection of residential terminal appliances, so they are sometimes called household circuit breakers. If we count from the time when this component was first invented, the circuit breaker product has a development history of nearly 120 years. Judging from the current development trend in the market, digitalization and intelligence are injecting new development momentum into this product. This article aims to reveal the key concepts and selection points of low-voltage miniature circuit breakers through a comprehensive explanation of miniature circuit breakers, so that everyone can have a deep understanding of this product and experience the beauty of low-voltage electrical appliance applications.
1. Milestones in the development of low-voltage circuit breakers
In 1879, the great inventor Thomas Edison proposed an initial idea for a circuit breaker product.
In 1900, Granville Woods improved the design and invented the automatic circuit breaker product.
In 1904, Cutter Manufacturing Co. in Philadelphia, USA, mass-produced circuit breakers.
In 1925, the NEC organization stipulated that circuit breakers were enclosed and able to be operated externally.
In 1932, Westinghouse Electric introduced the modern molded case air circuit breaker to the market.
In 1973, electronic trip products appeared on the market.
2. Introduction to miniature circuit breakers
A miniature circuit breaker (MCB) is an automatically operated electrical switch that contains a complete housing in a molded insulating material. It is used to protect low-voltage circuits from damage caused by excessive current generated by overload or short circuit. That is, when the current (MCB) passing through it exceeds the set value, it automatically disconnects (the connected circuit). If necessary, it can be switched between the ON and OFF states manually like an ordinary switch. In short, the miniature circuit breaker product has the dual attributes of a switch and a circuit breaker.
The rated current of the miniature circuit breaker is usually up to 125 A, there is no adjustable tripping characteristic, and the protection method in operation adopts thermal or thermal magnetic protection.
The miniature circuit breaker is a time-delay tripping device, and the size of the overcurrent controls the action time. This means that as long as the overload occurs for a long enough time to cause danger to the protected circuit, the line protection mechanism will work. Therefore, the miniature circuit breaker does not respond to transient loads such as switching surges and motor starting currents. When an overcurrent fault occurs, the miniature circuit breaker is usually designed to trip within 2.5 milliseconds. In the case of temperature rise or overheating, the circuit breaker may take 2 seconds to 2 minutes to trip (depending on the current level in the line).
The typical appearance of the miniature circuit breaker has different structures of single-pole, double-pole, three-pole and four-pole. In most cases, when the miniature circuit breaker is connected as a two-pole or three-pole, a fault in such a line will disconnect the entire circuit, providing complete circuit isolation. This feature will be helpful in the case of a single phase in three-phase motor protection.
Some view that the miniature circuit breaker is a better choice than the fuse because it does not need to be replaced once an overload is detected. Unlike fuses, miniature circuit breakers can be easily reset, which improves the safety of operation and greater convenience without incurring large operating costs.
3. Electrical symbol identification of miniature circuit breakers
The following symbol is usually used to represent the miniature circuit breaker product on the design drawings of low-voltage electrical or electrical equipment drawings:
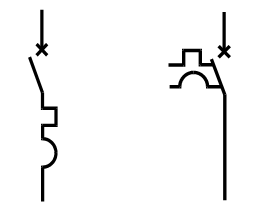
Miniature circuit breaker symbol
4. Working principle of miniature circuit breakers
There are two modes of operation of miniature circuit breakers. One is the thermal effect of overcurrent, and the other is the electromagnetic effect of overcurrent. The thermal operation of the miniature circuit breaker is achieved by a bimetallic strip, which is heated and deflected by bending whenever a continuous overcurrent passes through the miniature circuit breaker.
This deflection of the bimetallic strip releases the mechanical latch. Since this mechanical latch is connected to the operating mechanism, it opens the MCB contacts.
That is a simple explanation of how a MCB works. But in a short circuit situation, the sudden rise in current causes an electromechanical displacement of a plunger associated with the MCB’s trip coil or solenoid. The plunger strikes the trip bar, causing the latch mechanism to release instantly, opening the breaker contacts.
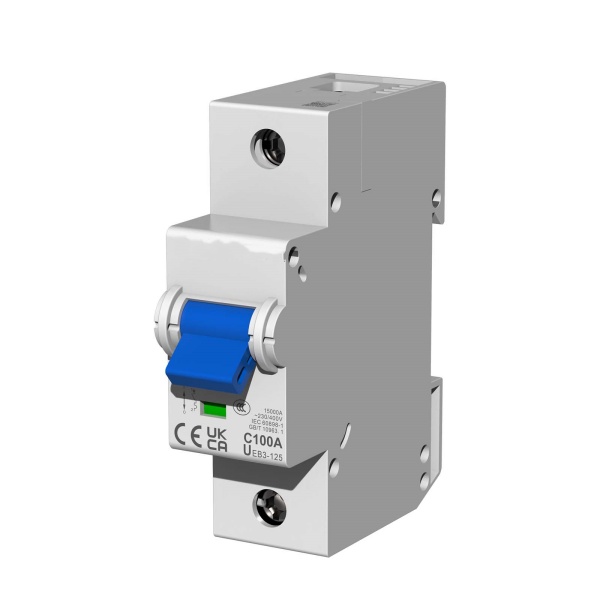
UEB3-125 MCB Miniature Circuit Breaker
Miniature circuit breakers (MCBs) are core components of electrical safety and have the ability to automatically disconnect overload or short-circuit currents. From historical development to modern intelligence, MCBs have been continuously optimized to provide stable and reliable circuit protection. When selecting an MCB, the rated current and protection characteristics must be considered to ensure that it matches the application scenario. Compared with fuses, MCBs are easy to reset, which improves the safety and economy of operation. With the continuous advancement of technology, miniature circuit breakers will continue to ensure the safety and efficiency of electrical systems.
Post time: 7 月-22-2024


