In modern society, the stability of power supply is crucial to ensure the normal operation of production, finance and people’s daily life. Automatic transfer switch, referred to as ATS, is a key device to ensure the continuity and reliability of emergency power supply system. Its performance and reliability are directly related to whether important loads can be guaranteed at critical moments. This article will introduce the working principle, composition and selection of relevant technical parameters of ATS in detail to help readers fully understand this important equipment.
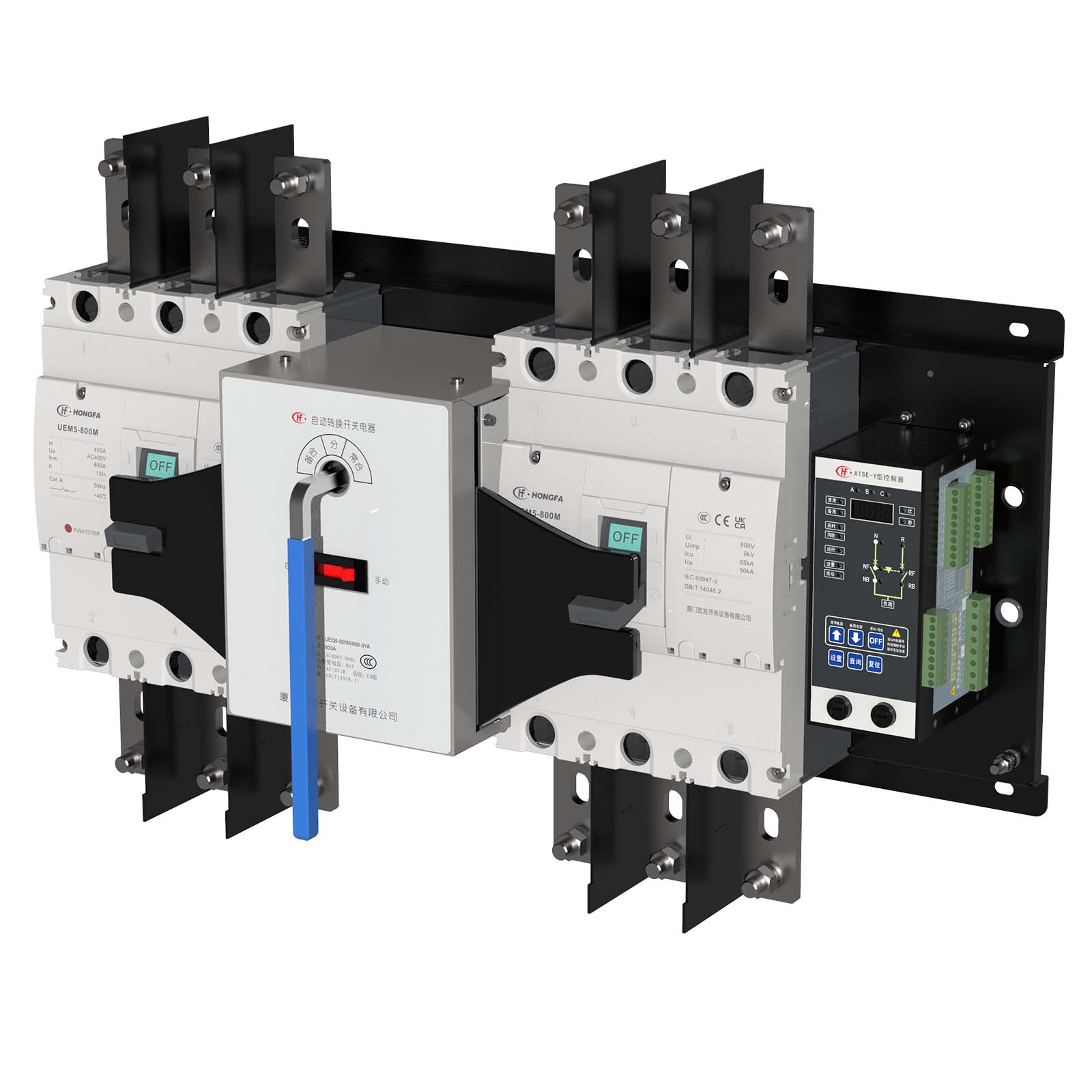
Automatic Transfer Switch UEQ5 series
1. Overview of working principle
Automatic transfer switch is referred to as ATS, which is the abbreviation of Automatic Transfer Switch.
Automatic Transfer Switch is mainly used in emergency power supply system to automatically switch the load circuit from one power source to another (backup) power source to ensure the continuous and reliable operation of important loads. Therefore, Automatic Transfer Switch is often used in important power consumption places, and its product reliability is particularly important.
Once the conversion fails, it will cause one of the following two hazards: short circuit between power sources or power failure of important loads (even short power failure), and the consequences are serious. This will not only bring economic losses (production suspension and financial paralysis), but also may cause social problems (life and safety are in danger). Therefore, industrially developed countries have listed the production and use of automatic transfer switch electrical appliances as key products and restricted and regulated them.
2. Composition of Automatic Transfer Switch
Automatic Transfer Switch generally consists of two parts: switch body + controller. The switch body is divided into PC level (integrated type) and CB level (circuit breaker).
(1)PC level: integrated structure (three-point type)
It is a special switch for dual power switching, with the advantages of simple structure, small size, self-interlocking, fast switching speed (within 0.2s), safety and reliability, but it needs to be equipped with short-circuit protection electrical appliances.
(2)CB level: Automatic Transfer Switch equipped with overcurrent release
Its main contacts can be connected and used to disconnect short-circuit current. It is composed of two circuit breakers plus mechanical interlocking, and has short-circuit protection function;
The controller is mainly used to detect the working condition of the monitored power supply (two lines). When the monitored power supply fails (such as any phase failure, undervoltage, loss of voltage or frequency deviation), the controller issues an action command, and the switch body automatically switches from one power supply to another with the load. The capacity of the backup power supply is generally only 20%~30% of the capacity of the common power supply.
The controller of the Automatic Transfer Switch should generally have a non-critical load selection function. The controller also has two forms: one is composed of traditional electromagnetic relays; the other is a digital electronic intelligent product. It has the advantages of good performance, adjustable parameters and high accuracy, high reliability, and easy use.
(3)Comparison of CB-level and PC-level ATS performance
The mechanical design concepts of the two are different
The CB level is composed of circuit breakers, and the circuit breaker is responsible for breaking the arc, requiring its machinery to trip quickly. Therefore, the circuit breaker mechanism has the problem of slipping and re-buttoning; while PC-level products do not have this problem. The reliability of PC-level products is much higher than that of CB-level products.
The circuit breaker does not carry short-circuit withstand current, and the contact pressure is small
When a short circuit occurs in the power supply circuit, the contacts are repelled to limit the current, thereby breaking the short-circuit current; and the PC-level Automatic Transfer Switch should withstand an overload current of 20Ie or more. The contact pressure is large and it is not easy to be repelled, so the contact is not easy to be welded. This feature is particularly important for fire power supply systems.
There is a problem of power superposition during the conversion process of the two power supplies
PC-level ATSE fully considers this factor. The electrical clearance and creepage distance of PC-level ATSE are 180% and 150% (standard requirements). Therefore, PC-level ATSE is safer.
The selection angle of contact materials is different
Circuit breakers often choose silver tungsten and silver tungsten carbide materials to match, which is conducive to breaking the arc.
However, this type of contact material is easy to oxidize, and the spare contacts are exposed to the outside for a long time, which is easy to form oxides that hinder conductivity and are difficult to remove. Once the spare contacts are put into use, the temperature rise of the contacts increases, which can easily cause the switch to burn out or even explode; and the PC-level ATSE fully considers the consequences of contact material oxidation.
4. Relevant parameter selection of PC-level Automatic Transfer Switch
Category selection
Currently, there are two usage categories of PC-level Automatic Transfer Switch in the Chinese market. One is suitable for AC-33B; the other is suitable for AC-31B; the usage category of the switch indicates its ability to control the load.
①. C-33B/A*: Applicable to mixed motor loads. It includes motors, resistance loads and incandescent lamp loads below 30%, the connection and disconnection current is 6Ie, COSj=0.5;
②. C-31B/A*: Applicable to non-inductive or slightly inductive loads, the connecting and disconnecting current is 1.5Ie, COSj=0.8; (*B: indicates infrequent operation; A: indicates frequent operation.)
Since it is difficult for Automatic Transfer Switch to pass the AC-33B test, some manufacturers lower the requirements for switch use and choose the AC-31B use category. Obviously, it is safer and more reliable to choose Automatic Transfer Switch using AC-33B than to choose ATSE using AC-31B.
Small-capacity Automatic Transfer Switch (≤100A) usually directly converts motor loads (such as fire pumps), and it is best to have AC-3 indicators (directly connect and disconnect squirrel cage motors), and be assessed according to the requirements of connecting 10Ie/disconnecting 8Ie/COSj=0.45. It is safer to use this product.
Short-circuit protection device selection
PC-level Automatic Transfer Switch does not have short-circuit protection function, so it needs to be equipped with short-circuit protection devices.
There are generally two types of short-circuit protection devices, fuses or circuit breakers. Since fuses have good current limiting performance and strong short-circuit current limiting capability, they are often used in places where the system has a large expected short-circuit current; while circuit breakers have poor current limiting performance and low rated short-circuit current limiting capability. The rated short-circuit current specified by ATSE products of different companies is different. The following table shows the rated short-circuit current specified by RTQ1 (TP1) automatic transfer switch electrical appliances.
When selecting the rated current value of short-circuit protection electrical appliances, the general principle is that the rated frame current value of the short-circuit protection electrical appliance (fuse or circuit breaker) is consistent with the rated frame current value of the protected electrical appliance (ATSE) (i.e. 1:1).
Segment and three-stage selection
The main contact of the two-stage Automatic Transfer Switch has only two working positions, namely the “normal power supply position” and the “backup power supply position”. The load will not experience long-term power outages, the power supply reliability is high, and the switching action time is fast.
The main contact of the three-stage ATSE switch has three working positions and multiple “zero positions (referring to the electric state)”, that is, the main contact is in neutral, and the load power-off time is relatively long, which is 2-3 times the power-off time of the two-stage type.
The three-stage “zero position” is mainly used for “temporary stop” to avoid impact current when the Automatic Transfer Switch is switching with high inductive reactance or large motor loads; it is not used for isolation during load maintenance. Isolation during maintenance must choose an isolating switch, which is safer. Because the isolating switch must have the following functions: ① The moving contact can be locked or visible when in the disconnected position; ② It has a higher rated impulse withstand voltage (1.25 times); ③ In any case, the limit leakage current should not exceed 6mA.
5. ATS action time selection
There are 5 action times to measure the conversion speed of an Automatic Transfer Switch (see GB/T14048.11). ATSE should provide users with at least one action time to facilitate users to choose according to their use requirements.
Contact conversion time
Measure the time from the first set of main contacts disconnecting the normal power supply to the second set of main contacts closing the backup power supply.
Switching action time
Measure the time from the moment the main power supply is detected to the moment the main contact closes the backup power supply (including the mechanism action time), excluding the delay introduced by the controller.
Total action time
The sum of the switching action time and the delay introduced by the controller.
Return switching time
The time from the moment the common power supply is fully restored to normal to the moment a set of main contacts close the common power supply plus the delay introduced by the controller.
Power failure time
Measure the switching process time from the moment the arc of each phase is finally extinguished to the moment the main contact closes another power supply, including the delay introduced by the controller.
General users should pay attention to the “total action time” or “conversion action time” to meet the requirements of different power distribution systems. The total action time of two-stage PC-level ATSE is generally 50-250ms;
The total action time of three-stage PC-level ATSE is generally 350-600ms;
The total action time of CB-level ATSE is generally 2000-3000ms.
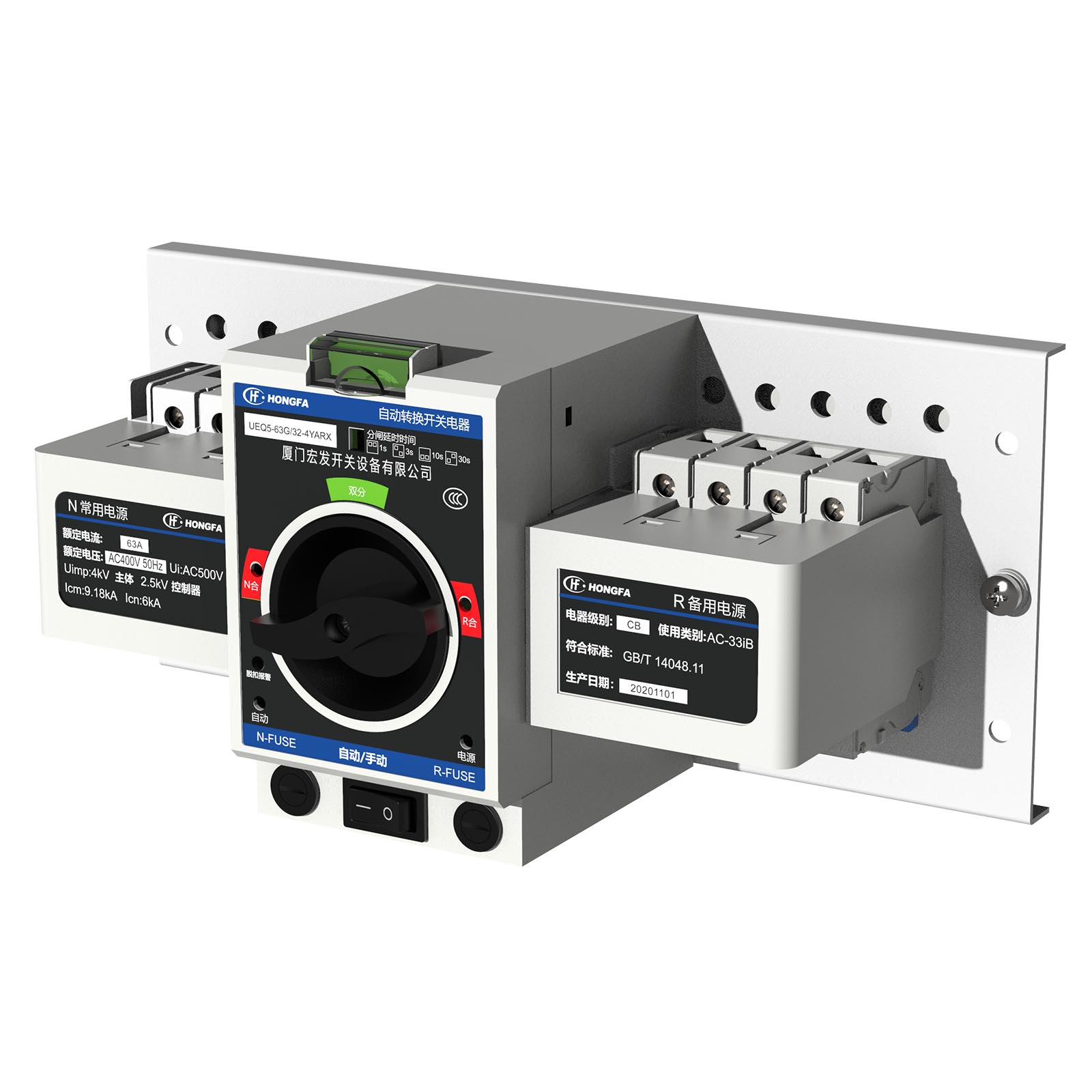

The UEQ5-series of Automatic Transfer Switch
Through the above in-depth analysis of ATS, we can clearly understand the core role of ATS in modern power systems. ATS not only needs to quickly and accurately switch between the main power supply and the backup power supply to cope with sudden power failures, but also ensure safety and reliability throughout the conversion process. Whether it is PC-level or CB-level ATS, they each have unique design concepts and application scenarios. Choosing a suitable ATS is crucial to ensuring the continuous power supply of critical power loads.
Post time: 7 月-12-2024


